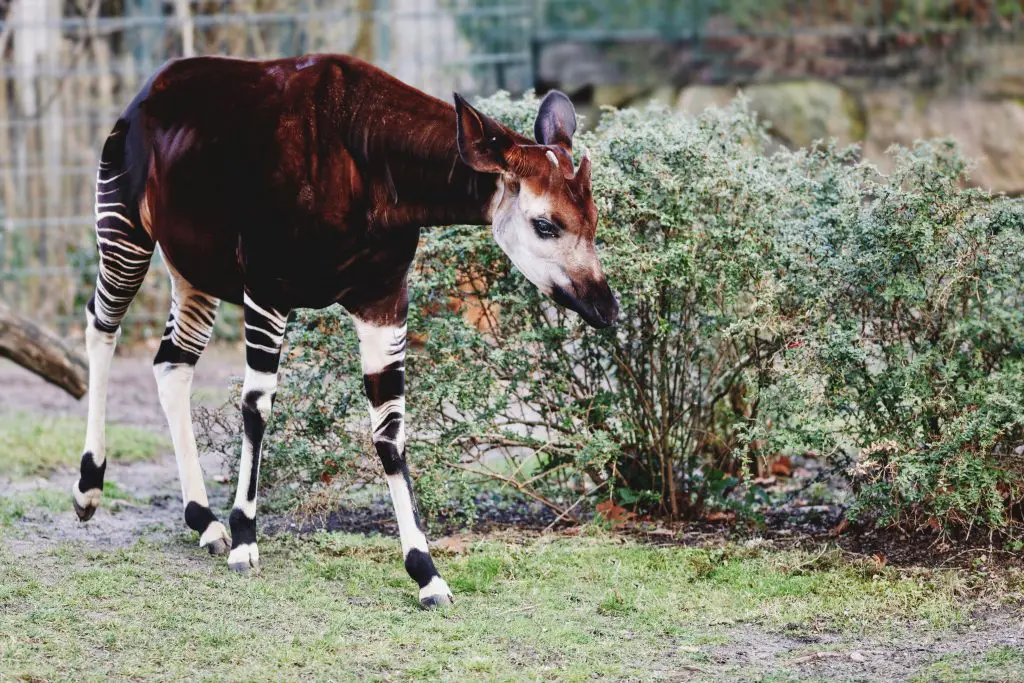
A native of the Democratic Republic of Congo, the okapi is an animal that resembles the zebra and the deer. It is an endangered species with many of its animals having been tamed. The okapi is pronounced as oh-KAHP-ee.
Where can you find okapi?
The Democratic Republic of Congo is known for its wide and dense forests; here, one is going to find an okapi. Dense forest are a fertile ground for the flourishing of flora and fauna. This is because human beings shy away from colonizing such habitats thereby giving flora and fauna more peace and a higher chance of survival.
The Okapi Wildlife Reserve is located in Ituri Forest, DRC. UNESCO estimates that the wildlife reserve hosts a whopping 5000 okapis. This is a heritage site and is one of the most unique and serene places in the world. The wildlife reserve is an epicenter for research and conservation. The color and the physical features of the okapis make them blend in the dense rainforest. The zebra uses its stripes in order to shoo away the flies; the okapi uses the stripes in order to blend in the sun-dappled trees.
DRC (Ituri Forest) is the only place where the okapis can be found in the wild. If one is interested in seeing the okapis, one can explore a number of tourist destinations. The Maryland Zoo hosts a male okapi as part of the African Journey.
In 1956, the okapi was introduced in the San Diego Zoo. This was a gift given to the zoo by Belgian Congo (now DRC). Five years later, the zoo celebrated the birth of Baruti. In 1978, a male and female okapi were introduced to the zoo’s counterpart, the San Diego Safari Park.
Nashville Zoo hosts the okapi known as Kwasi. The main purpose of behind-the-scenes animals at Nashville Zoo is research as well as breeding. Just like the okapi in the wild which prefers exclusion, the Okapi at the Nashville Zoo lives on its own. Visitors notice that it is a shy and nervous animal.
Outside the USA, London Zoo has an okapi known as Oni. The Zoo welcomed a baby okapi named ede which was born by Oni. The beautiful and adorable baby girl excited the staff on the zoo and happily welcomed it.
Ueno Zoo in Tokyo is one of the few places in Asia where one can see the okapi. The okapi was introduced to the zoo on 6th March, 2018. Another zoo where one can find an okapi is the Kanazawa Zoo in Yokohama. The zoo has a dedicated exhibit for the African habitat, and thus, it has taken the okapi as one of its treasured African animals.
Other places where one can see an okapi include Copenhagen Zoo, Lisbon Zoo, Berlin Zoo, and Cologne Zoo.
What is an okapi a cross between?
The okapi is otherwise known as a forest giraffe. The mammal looks like a breed cross between a zebra and a deer. The okapi has stripes that resemble that of the zebra. Scientists regard the okapi as a primitive deer.
How was the okapi named?
The word okapi is derived from the Lese tribes, subsistence farmers living in the Ituri forest. This community referred to this species as the o’api’. This is a compound word derived from two words. The first word is oka which means to cut, and the second word is kpi which refers to a design that is made on pygmy arrows by wrapping the arrow with the bark in order to leave stripes when it is scorched by the fire. The stripes which are located on the legs of the okapi have a resemblance with the stripes on the shafts of the arrow.
Is The Okapi Related to Zebras?
There is limited information on the physiology as well as the anatomy of the okapi. However, data on this has become available over the years. There is an assumption that the okapi is related to the zebra. This is due to the black and white stripes on the buttocks and their legs. The stripes in the okapi should not fool someone that they are closer to the zebra. The okapi is actually more related to the giraffe than it is related to the zebra.
If one carefully looks at the head of the okapi, then, one is going to see a strong similarity between the okapi and the giraffe. The okapis are the only relative of the giraffe which is now living. The other relatives of the giraffe have become extinct. The giraffe and the okapi are categorized under the giraffids.
What is the Similarity Between a Giraffe and an Okapi?
The okapi has many similarities with its towering cousin, the giraffe. Both the okapi and the giraffe have short and cloven hooves. Of course, the giraffe wins the contest when it comes to the height of the neck. Both the giraffe and the okapi have identical skulls. The two animals rest their weight on the two toes. The major difference between the giraffe and the okapi is that the giraffe is a herd animal while the okapi prefers being a loner.
How many okapis are left in the world and are they rare?
There is no reliable data and information about the population of the okapis. Researchers note with concern that in the last two decades, the population of the okapis has been slashed by a half. It is estimated that the total population of the okapis ranges between 10, 000 and 20, 000, but it is difficult to put this data to a test. One of the reasons why scientists find it difficult to study the okapis and learn about their demographics is that they are secretive animals.
Threats to the population of the okapis are related to deforestation and the encroachment of the forest. These include logging, human settlements, and mining. DRC has been vulnerable to rebel attacks and this has greatly reduced the population of the okapis. The International Union for Conservation of Nature states that the okapi is an endangered species.
In order to study the okapis on their behavior and the demographics, stakeholders in DRC launched a camera program that would help in studying the okapis. The team consisted of ICCN rangers, the pygmy guide, and the community. The scope of this study includes trying to determine the population of the okapi and trying to capture the behavior of the okapi. The effort has come up with interesting observations.
Are okapis aggressive?
The okapi is an animal of tranquility, and therefore, they are not typically aggressive. However, the okapi is known to mark its territory and desires to have its own space, and it can do this aggressively. For instance, the okapi can show aggression through kicking around or hitting the franks of the opponent with the head or its horns.
The okapi marks its territorial space by spraying the desired area with urine. In order to show its dominance in a certain territorial space, the okapi raises its head with confidence. An interesting thing with the okapi male is that it will aggressively defend its territory from other males, but when it comes to the female okapi, it allows them to pass through.
What do Okapis Eat?
The okapis is a herbivore. Thus, they take a plant-based diet that includes twigs, leaves, fruits, buds, and other types of vegetation. Its long and dark tongue helps it to strip the leaves from the plants and the trees. Its digestive system is related to that of the cow and the giraffe- it has four stomachs making it manage to digest tough forest plants. In a single day, the okapi can eat as much as 43 kg of leaves.
The okapi’s ecological environment is the primary or secondary type of forest. Their main diet is understorey foliage from the dense rainforest. The okapi does not inhabit the forest savannah. They have a preference for treefall gaps. Okapis also eat fungi.
Like any other animals, the okapis have to think about salts and minerals so that they can meet their nutritional needs. The okapis eat on the red clay that is found in the forest, thereby providing it with the much-needed salts and minerals. One of the unique things about the okapi is its ability to eat some plant species which are poisonous to the animals of the forest.
When was the first okapi found?
The enigmatic and mysterious okapi is one of the oldest mammals to inhabit the earth, but it is only in the early 20th century that the first okapi was identified. The first okapi became known to the world in 1901. Around this time, the okapi was merely a subject of rumors without any confirmation or scientific study. The lack of sightings, as well as embellished descriptions, gave the okapis a mythical quality.
Though the existence of the okapi was recognized in 1901, early European contact with the Africans did not miss the mention of the okapi. For example, Henry Morton Stanley experiences of 1887 do mention a type of a donkey, and this was later clarified to be the okapi. The natives of DRC would often catch the okapi in their traps.
What Other Names Does an Okapi Have?
The okapi has been nicknamed the forest giraffe or the rainforest zebra. This is because of its black and white stripes on the upper legs and the buttocks. Others call the okapi the African unicorn.
What Sound Does an Okapi Make and How do the Okapi Communicate?
A baby okapi is simply known as a calf. The adult okapi does not do much vocalization. The only time it vocalizes much is the time it is ready for breeding. Calves are more active when it comes to sound, and they cough, bleat, and whistle when the mother is away. The okapi mother communicates with the calf through infrasounds. These are noises that are not detectable to the human ear.
The vocal sounds in the okapi are not well developed. This leaves the mammal with three main vocal sounds: chuff (a contact call which is used by the okapi male and female between them), moan (this sound is used by the female at the time of courtship), and bleating (this is used by the infant when it is stressed up).
The communication channels of the okapis are tactile and acoustic. They can also communicate through scent marks. The perception channels include chemical, tactile, and visual.
Can you Ride an Okapi?
It is not easy to ride an okapi for four main reasons.
First, the okapi is an elusive and secretive mammal. It does not like being close to human beings. Chances are very low that one will be able to get near the okapi in its natural habitat. Even if one was to get that chance, the okapi will simply not feel comfortable.
Second, if one is able to ride an okapi, one might keep on sliding off.
Third, unlike a horse that has a controllable temper, the giraffe, the zebra, and the okapis have a high temper, and therefore, one cannot easily control it.
Lastly, if one goes to see the okapi at the zoo, the authorities will not let one ride an okapi. This is because the okapi is a highly protected animal due to the fact that it is rare.
Can you Hunt Okapi? (Its illegal)
It is not easy to hunt the okapi due to its camouflaging technique. This is because the okapi has distinctive stripes which are camouflage by breaking up the body’s outline in the forest’s shade and light. These stripes are unique to every okapi. Again, the authorities will not be comfortable with the hunting of the okapi. The only people who do hunt down various animals in DRC including the okapi are the pygmies. (DRC – The Democratic Republic of Congo)
Can you Eat Okapi?
Some communities in the world eat the okapi. The people living in the Southern part of Ituri forest consider the okapi meat as the most valued bush meat.
What is the weight of the okapi?
The okapi is one of the few mammals where the female is bigger than the male. Typically, the weight of an okapi is in the range of 200-300 kg. The okapi can be as tall as 6.5 feet and can have a length of 8 feet.
Can Okapis Swim?
The natural habitat of the okapi may not be having a large water body. This is because the okapi prefers to eat leaves, and naturally, it will prefer an environment with leaves. However, if need be, the okapi can swim.
Can Okapis Jump?
Yes, an okapi can jump. This is more so when you are dealing with a calf. The okapis can also jump when they are playing.
How Fast can Okapis Run?
The okapis have a very strong sense of coming danger. When they hear the slightest hint of danger coming, they do run away fast. This is a wary animal and is going to disappear to the forest upon noticing any threats. The okapi can run at a speed of 60 km/per hour.
How do Okapis Defend Themselves?
Just like the giraffe, the okapi has upright and large ears, and therefore, it is able to pick any coming danger in preparation for self-defense. Though not common, the okapis can stay in groups. This will help them in the case they are attacked. The female okapi is very protective of its calf.
When it senses potential danger, it beats the ground with the hooves. Because the okapis have large ears, they are able to sense danger early enough. Because the okapis have dark bodies, they are able to hide in the forest and the predators cannot easily spot them. They hide or run.
What are the Okapis Predators?
First: The leopard is a major predator to the okapi. As a matter of fact, the leopard is the only natural predator to the okapis. So threatening is the leopard to the okapis that the okapis spend their lives evading the leopards. Other cats such as the servals as well as the golden cat prey on the okapi, though this is not a common occurrence.
Second: Poaching remains a major threat to the okapi. They are poached for their meat and their skin. It should be noted that the Mbuti pygmies rely on the forest in DRC for their day-to-day water, firewood, natural resources, and medicinal plants. What these activities do is that they lead to the fragmentation of the natural habitats inhabited by the okapis.
In 2012, armed militias attacked Okapi Conservation Project and killed 6 people and 13 okapi (the 14th okapi would die a few days later as a result of the wounds from the attack). This was the first attack by rebels that targeted the okapis at the Epulu center.
What is Okapis Scientific Name?
The classification of the okapi took several years of evolution. The locals reported that they were seeing a striped zebra. As a matter of fact, scientists were attempting to classify an animal that they have not yet seen. Originally, the scientists categorized the okapi as the Equus due to its strong similarity with the zebra and the horse.
It is possible to gather a lot of information through fossil records. Unfortunately, in the case of the okapis, there is not much fossil information available about the okapis.
Today, thanks to more research and better research strategies, much is known about the okapis. The scientific name for the okapis is Okapia johnstoni. The okapis are categorized as a mammal. The following is the basic taxonomy of the okapis:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Genus: Okapia
- Class: Mammalia
- Family: Girrafidae
What is the Ecology of the Okapis?
The okapis live in places that are solitary. In Ituri Forest, the plants grow so big that they can engulf an animal. In its habitat, the sun does not penetrate through the dense forest and the animal may feel wet. They live in a high and canopy rainforest where they can find the understory foliage. The okapis live in an attitude of 1600 to 3200 ft above sea level.
The okapi is found in the north as well as the east of the Congo River. These include the river basins of Ebola, Rubi, and Lake Tele. Whereas Uganda used to host the okapi, this species has become extinct there. The okapi is not going to live in a swamp settlement or a gallery forest. In particular, the swamp contains a wet substrate which the okapi does not like.
There is a big difference between the migratory behaviors of the okapis. On one hand, the male okapis do migrate continuously. On the other hand, the female okapi prefers a sedentary lifestyle.
Human factors such as mining, logging, and human settlement push the okapis away from their natural habitat. What this means is that relocating means that they live in areas that are less desirable for their optimal living conditions. Again, when they live in less desirable conditions, their chances of survival and reproduction is reduced.
How do the Okapis Adapt to the Environment?
The coat of the okapis helps it to withstand wet weather conditions and is waterproof in itself. The coat of the okapi is very oily, and this helps it in wicking the water in the tropical rainforest.
How Long can Okapi Live?
The okapi becomes sexually mature at the age of 2 years. When in captivity, the lifespan of the okapis is 30 years. Being in the wild means that they are vulnerable to attacks by the leopards. Due to this, the researchers estimate that the okapis have a lifespan of 15 to 30 years in the wild. The highest recorded age of the okapi is 33 years.
The major cause of death among the okapis in their natural habitat is of course predation. Other causes include age, fungal diseases, bacterial infection, viral diseases, parasites, worn teeth, arthritis, and overgrown hooves.
How do an Okapi Sleep?
The okapi sleeps at night and is active during the daytime, and thus, they are diurnal animals. However, it is not uncommon to find them feeding at night. The okapi can sleep in short episodes, as little as 5 minutes.
Do Female Okapi have Ossicones? (Horns)
The male okapi has horn-like structures which are known as the ossicones. They are covered by the skin and extended from the head. This is a characteristic that they share with the giraffe. The ossicones are not found in the females the female has hair whorls. Having stated that, the okapis are dimorphic mammals. This means that there is a clear and visual difference between the male okapi and the female okapi.
Can Okapi and Giraffe Breed?
The answer is simply no, the okapi and the giraffe cannot breed. Scientists have presented the conditions that ensure that one animal can breed with the other. The first condition is that the two animals should have similar chromosomes, or should have near-similar chromosomes. Second, the genes should be the same or nearly the same.
Though the okapi and the giraffe colonize the same habitat, they are too different to inter-breed. There are mere relatives without the ability to interbreed.
Can Okapi Breed with Zebra?
Whereas the chromosome count of the okapis is similar to that of the zebras, the two cannot simply inter-breed. It should be noted that the okapis are known to produce some abnormal sperms, which are not going to be compatible with the zebra in the reproduction process.
Can Okapi be Domesticated?
There have not been attempts to domesticate the okapi, such efforts are not only a lofty goal but also unrealistic. There are various challenges to the domestication of the okapi. To start with, it is an endangered species. What this means is that the authorities are not going to be comfortable with individuals seeking to own an okapi.
Second, the okapi prefers a wild and expansive natural habitat. In addition to that, it will need to feed on different types of plants that are not easily available. The cost of acquiring an okapi, assuming this was possible, is high, and so is the cost of maintenance. One of the reliable sources of the okapi is a donation to the government of DRC, and it is unlikely that such a donation would be given to an individual.
How is the Reproduction on the Okapi?
Due to the fact that the okapi is an elusive mammal, mating has not been observed in their natural habitat. However, their mating behavior has now been observed in captivity.
The male and female okapis do not stay together for long, and they do not give each other much company. As a matter of fact, the male and its counterpart the female okapi come together only at the time of mating. The courtship process in mammals is characterized by circling, licking, and smelling each other. The male okapi shows its interest in mating by extending its long neck, tossing the head, and producing its leg forward. Consequently, the male okapi mounts and copulate.
The okapis do not consider a commitment or a lifetime relationship. After mating, each individual goes its separate ways. A female okapi carries one calf for every pregnancy. Its gestation period takes roughly 450 days. During the gestation period, the udders of the female okapi swells, this starts two months before delivery. For the purpose of giving birth, the female okapi goes deep into the forest.
What do you call a baby okapi?
A baby okapi is simply known as a calf (plural calves). For about two months after birth, the offspring is hidden a heap of foliage. The mother goes out to look for food then comes back to nurse the offspring. Six months after birth, the female leaves the calf to start feeding for itself and become independent. There are a few cases, though, where the okapi rejects it’s newborn and kicks it.
The okapi does not wait for the mother for parental investment. In particular, the role and the responsibility of the male okapi starts and ends with insemination.
Are okapis Social Animals?
The okapis are not social animals. They are elusive and may feel more comfortable in exclusivity. The okapis are not known to seek a companion. The okapis may feed with other animals for a short time, then go on their own. The okapi prefers a large and secluded area. With the rainforest shrinking, this is becoming more difficult for them.
In the life of the okapis, a hierarchy has been observed. The animals which are dominant are known to raise their heads on the ground. The submissive okapis place the head on the ground.
Are okapi an endangered species?
It is not easy to determine if the okapi is an endangered species or not. This is because an animal can only be declared endangered if its total population is known, and in the case of the okapi, there are varying figures of the animal’s total population. Nevertheless, there is a general consensus among the conservation groups and the scientists that the okapi is a vulnerable animal.
In 2013, IUCN classified the okapi as near threatened. This is a category that qualifies a species as not threatened at the moment but has all the likelihood of being threatened in the future. One parameter that qualifies a species as near threatened, and this was noted in the okapi as much, is the drastic reduction of a species. Consequently, the okapi was later classified as threatened by the scientists citing threats to the animal, drastic decline in total population, and poor conservation efforts.
Are there any instances of same-sex behavior in okapis?
Can animals exhibit same-sex behavior?? Yes, same-sex behavior has been documented in various species, including Okapis. These elusive creatures, native to the rainforests of Central Africa, have been observed engaging in same-sex mounting and genital contact. This behavior may serve various purposes, such as social bonding or competition for resources. Same-sex behavior is a natural occurrence that exists beyond human society.
Now Where From Here?
From the data and information about the okapis, there is more need for research on this mammal. The research can be aided by three main groups of people. The scientists are well versed with the most effective research methodology in order to arrive at informed findings. Donors who should give the much-needed funding. Lastly, the tourists and the local community can play a critical role in giving out the information they spot about the okapis.
In addition to that, there ought to be a more aggressive effort towards conservation. The okapis are an endangered species. Strategies of conservation include preventing armed conflicts and empowering the local community with alternative means of sustenance. It is only these efforts that can save the okapi species.







